Satellite/GPS Repeater Solutions by Global Foxcom
In places where there is no terrestrial infrastructure, satellite phones fill the gap. However, this requires line-of-sight to a satellite.
What happens when the satphone user needs connectivity underground or indoors, and stepping outside to make the call is not an option? So too with testing avionics inside an aircraft hangar. Pulling the aircraft outside is both costly and time consuming.
Turnkey Benefits of Global Foxcom’s Hangar Repeater Solution
Save Time
Lower Fuel costs
Save Manpower
Lower Heating and Cooling costs
Increased Operational Effectiveness
24/7 Monitoring
Our Technology
GPS Repeater FAQs
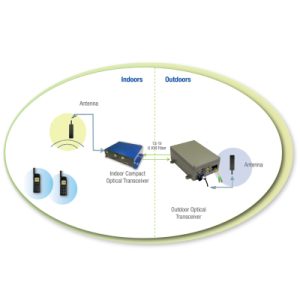
A GPS repeater is a device that receives GPS satellite signals from an external antenna and rebroadcasts them inside a building, vehicle, or other enclosed spaces where GPS signals are weak or unavailable.
A GPS repeater consists of three main components:
- External Antenna: Captures GPS satellite signals.
- Repeater Unit: Amplifies and transmits the signals.
- Indoor Antenna: Rebroadcasts the signals to GPS receivers inside the covered area.
GPS repeaters are used in:
- Aircraft hangars
- Underground facilities
- Tunnels and parking garages
- Large buildings
- Military and defense applications
- Test and development labs for GPS equipment
No, GPS repeaters function independently of the internet. They only relay GPS signals, which are transmitted by satellites.
In many countries, the use of GPS repeaters is regulated and may require a license. Always check local regulations before installation.
- GPS Repeater: Captures and retransmits GPS signals without modification.
- GPS Booster: Amplifies weak GPS signals to improve reception.
A GPS repeater allows GPS devices to maintain signal lock indoors, but it does not enhance the accuracy of GPS positioning.
The coverage area depends on the repeater’s power output, typically ranging from a few meters to tens of meters.
Improper installation or excessive signal amplification can cause interference. It is crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines and regulatory standards.
Installation typically involves:
- Mounting the external antenna in a location with a clear view of the sky.
- Running coaxial cable from the antenna to the repeater unit.
- Positioning the indoor antenna in the desired coverage area.
- Powering the system and testing GPS reception.
Yes, as long as the GPS device operates on standard GPS frequencies (L1, L2, etc.), it should work with a GPS repeater.