What Is Earth Station Antenna Diversity – Benefits, Types & Use Cases
Earth Station Antenna Diversity refers to using two or more geographically separated satellite antennas (earth stations) to improve the reliability and availability of satellite communications. It is a strategy to mitigate disruptions caused by factors such as:
Why Use Earth Station Antenna Diversity?
- Rain Fade & Atmospheric Attenuation
- In Ku-band and especially Ka-band frequencies, heavy rain, snow, or storms can severely weaken (attenuate) the satellite signal.
- By placing antennas at two locations separated by tens or hundreds of kilometers, it’s unlikely that both will experience the same severe weather simultaneously.
- Physical Obstructions or Site Issues
- Local interference, physical blockage, or equipment failure at one site won’t necessarily affect the other.
- Improved Uptime (Redundancy)
- Diversity improves the overall link availability, often achieving the high uptime (e.g., 99.99%) required for broadcast, defense, or critical communications.
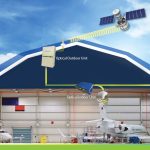
How It Works
- Two or more earth stations are connected to the same network.
- Each has a dish pointed to the same satellite (or sometimes different satellites providing the same service).
- A diversity switching system (or automatic uplink power control system) selects the best signal path in real time or combines the signals.
- Can be applied for uplink diversity, downlink diversity, or both.
To achieve this, operators often rely on RF over Fiber for carrying RF signals efficiently between sites.
Types of Earth Station Diversity
- Site Diversity
- Antennas are located at widely separated sites to avoid simultaneous weather impact.
- Antenna Diversity (on the same site)
- Two or more antennas in close proximity, less effective against large-scale weather but useful for load balancing or backup.
- Frequency Diversity
- Using different frequency bands (e.g., Ku and C-band) in parallel to overcome weather-specific attenuation.
- Polarization Diversity
- Using different signal polarizations to improve resilience.
Where It’s Used
- Satellite television broadcasting
- Teleports for corporate or government networks
- Military and defense satellite communications
- Data and internet backhaul over satellite
Combining earth station antenna diversity with advanced transmission technologies such as RF over Fiber ensures greater reliability for satellite communications.